Science
HepaRegeniX aims at curing liver diseases by reversing the disease path through liver regeneration. Along this path, the company is actively developing novel therapies for the treatment of both acute and chronic liver diseases.
Liver diseases face an enormous unmet medical need
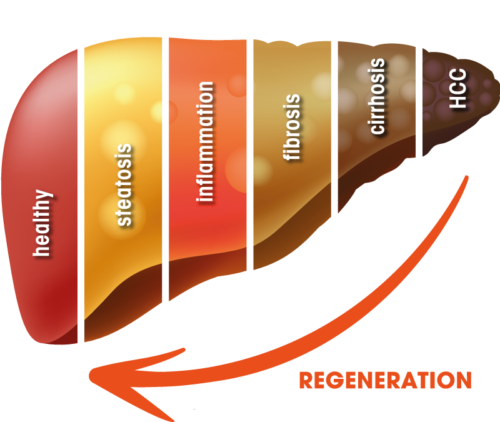
Liver diseases are characterized by a gradual deterioration of the liver function, and, on a molecular level, by a reorganization and destruction of liver tissue. Several disease stages characterize the path from the healthy liver to a fully developed hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The causes for these circumstances include but are not limited to long-term external or internal risk factors.
External risk factors include high-fat foods, excessive alcohol usage, toxins or infections. However, also autoimmune, genetic, and metabolic diseases can result in chronic liver dysfunction. 1,2
Millions of people are affected from these risk factors, for example:
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is increasingly recognized as a very wide-spread disease with estimates as high as 25 % of the population worldwide being affected. 3
- Risk factors for NAFLD and HCC include overweight, obesity and diabetes, affecting 2 billion and over 400 million adults, respectively.4
- Approximately 75 million people out of 2 billion regularly consuming alcohol worldwide are diagnosed with alcohol-abuse disorders and are at risk for alcoholic liver disease. 4
Alcoholic liver disease possibly being the chronic liver disease that is widest known.
Liver diseases today account for
- At least 250.000 patients suffering from an acute disease per year in EU5 and the U.S, and 700.000 patients from chronic liver diseases per year in EU5 and the U.S. 6
- 2 million or 3.5 % of worldwide deaths per year 4 with hepatocellular carcinoma as the most common primary liver cancer being considered fifth most common cancer and the third leading cause of cancer-related death in the United States. 7
These numbers illustrate the huge dimension of the unmet medical need in the liver field due to the lack of appropriate treatment options.
In order to fully meet this need, an unique and innovative approach is needed to treat a broad range of acute and chronic liver diseases, e.g. through MKK4 inhibition.
MKK4 – A First-in-class Therapeutic Target
HepaRegeniX’ approach is based on findings of Prof. Lars Zender and his research team at the University Hospital Tübingen, Germany. His laboratory identified Mitogen-Activated Protein (MAP) Kinase Kinase 4 (MKK4) as a key regulator of liver regeneration. Suppression of MKK4 gene expression by small RNA molecules demonstrated the regenerative capacity of hepatocytes even in severely diseased livers. 7 Prof. Zender and his group are important cooperation partners of HepaRegeniX still today.
Since 2017, HepaRegeniX has identified several small molecule inhibitors of MKK4 as part of its targeted drug discovery efforts. These molecules recently produced successful preclinical results in several animal models which led to start of clinical development for HRX-0215 as the first MKK4 inhibitor from the company´s small molecule-based liver regeneration platform. First proof for for pharmacologically induced benefits in non-rodent model in a collaboration with Mayo clinic were presented at AASLD 2020. In December 2020, it was shown, that treatment with selective Mitogen-Activated Protein (MAP) Kinase Kinase 4 (MKK4) inhibitors over a three-month period reduced hepatic steatosis and liver damage in a murine model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)-associated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). MKK4 inhibition was not only safe and well tolerated but even showed marked growth suppression of NASH-associated hepatocellular carcinoma.
Most, specifically, HepaRegenix was able to demonstrate that MKK4 inhibition causes
- An enhancement of hepatocyte proliferation in mice and pigs
- A general increase of hepatocyte robustness
- A significant reduction of alcohol-induced steatosis, chronic NASH and NASH-HCC
- A reduction of liver lipids without affecting body or liver weight and a prevention of tumor progression
In addition to a possible use in liver regeneration, HepaRegeniX recognizes potential for MKK4 inhibition in a range of other indications, including cancer. In this respect, the company has recently initiated a collaboration with NKI to investigate the use of MKK4 inhibitors for cancer combination therapy.
[1] https://www.healthline.com/health/liver-diseases (last accessed Nov 25, 2020)
[2] https://www.webmd.com/hepatitis/liver-and-hepatic-diseases (last accessed Nov 25, 2020)
[3] Younossi Z et al., Hepatology 2019 Jun;69(6):2672-2682. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30251
[4] Asrani SK et al., J Hepatol. 2019 Jan;70(1):151-171. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2018.09.014
[5] LifeSci Partners Liver Disease Assessments Deliverable for HepaRegeniX, June 2020
[6] Fingas CD et al., CLD 2016; 8(5):119-122; DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/cld.585
[7] Wüstefeld T et al., Cell 2013; 153(2):389-401; DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.03.026